Thesis: Predicting the longevity of resources shared in scientific publications
arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.12800
Github: https://github.com/UKGANG/tobit
This paper investigates the determinants of publications’ reproducibility and presents a novel approach to modeling the relationship between features and the target variable. We first established a baseline using classic machine learning techniques such as linear regression, lasso, ridge, elastic net regression, logistic regression, and random forest.
To improve the accuracy and generalization ability of the model, we proposed an advanced Tobit censored regression model using the MAP (maximum a posteriori) estimation.
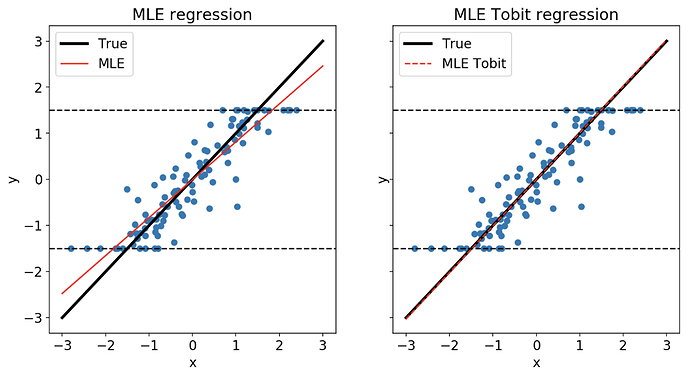
The comparison between the MLE regression and the Tobit regression
The Tobit regression model assumes that there are two latent variables on the left and right-hand sides that cannot be directly observed. Using maximum likelihood estimation, the model approximates the relationship between the features and the target variable. We further enhanced the model’s generalization ability by introducing an elastic net regularization term, which combined the Gaussian and Laplacian distribution as the prior probability to estimate the parameter of the Tobit model. This prior probability acted as an elastic net to increase the model’s generalization ability, and we used bootstrap aggregation to extract feature importance multiple times to obtain a robust rank of their estimations.
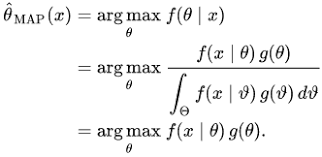
The MAP estimation formula
Our results demonstrate that the proposed Tobit censored regression model with elastic net regularization significantly outperformed the classic machine learning techniques in predicting publication reproducibility. We believe that our study provides a useful reference for researchers who seek to explore and understand the reproducibility of publications.
